
There are many, many programming languages available that allow us to program computers to solve all kinds of problems. There are scripting languages, systems languages, web programming languages, dynamic languages, object-oriented languages, functional languages, and the list goes on and on.
But did you know that all programming languages have 3 elements in common? Three very simple elements that give us the power to implement solutions to extremely complex problems.
These 3 elements are:
Sure, many programming languages have many other complex features. Some are ‘easy’ to learn and others more difficult to learn.
In this post I’d like to talk about each one of these elements and build a very simple C++ program that uses all of them. C++ is one of those languages that is considered very difficult to learn because it is very complex.
Let’s talk about each of these elements individually and we’ll write a simple C++ program along the way that uses all of them. We’ll keep this example simple and I’m sure you will be able to follow along.
If you’d like to follow along by typing or copying/pasting the code below, you can do so without installing any software at all. Simply point your favorite browser to https://www.onlinegdb.com/ and select C++17 from the dropdown list at the upper right.
Then delete the text in the online editor window and type or copy/paste the code we’ll write along the way.
When you are ready to run the program, simply click on the green Run button at the top of the screen.

If you see any errors, then double check that you entered the code exactly as shown and try it again. Once the program runs, you will be able to enter data and see output at the bottom of the screen.
So, what are these 3 elements all about?
It’s actually very simple. In order to solve problems with any programming language, we write code that tells the computer what operations to execute and in what order. The order must be very specific – remember the computer is not very smart – it simply follows our instructions. These operations make up what is called an algorithm. Just a fancy word that describes a set of operations that solves a specific problem. You can think of this very much like a cooking recipe. If you follow the recipe exactly, you will end up with the produce of that recipe.
Sequence, Selection, and Iteration are the basic elements that we use to tell the computer what to do. The code will definitely look different depending on the programming language we use, but the algorithm will be the same.
So let’s describe these elements:
That’s it, these 3 super simple elements give us the ability to write programs that solve problems. When we put them together we can create programs that are very complex such as operating systems, game engines, compilers, anything! In fact, with just Sequence, Selection, and Iteration we can implement any algorithm.
Read that again! Any algorithm! That’s a very powerful place to be!!
Alright, let’s write some C++ code together.
Let’s start with Sequence. Most programming languages simply execute instructions one after another as they are read – much like reading a recipe or a book.
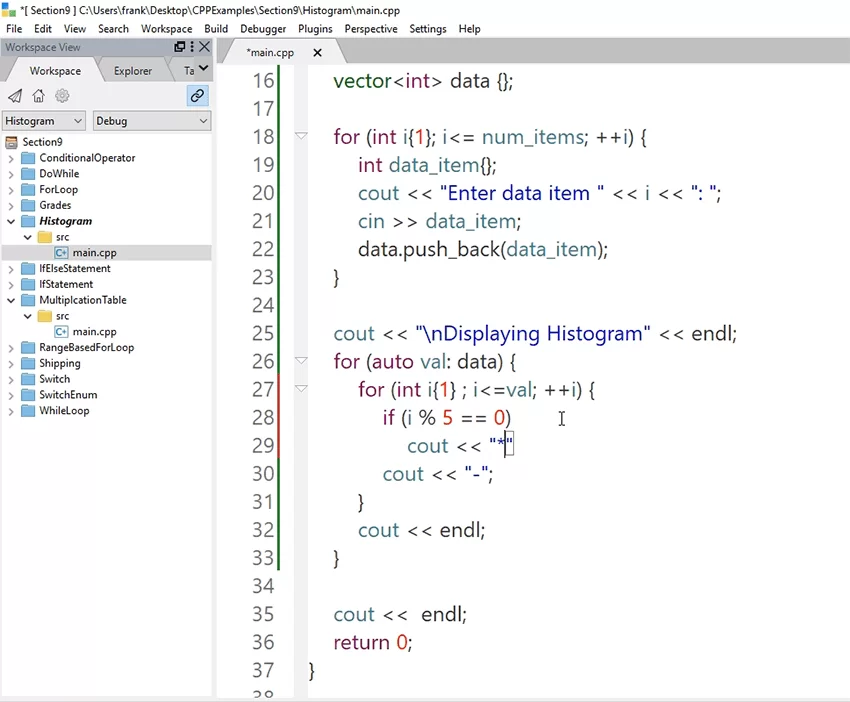
Here’s a simple C++ program that prompts the user to enter their age and then reads what they type in on the keyboard into a variable and then displays “Bye.” to the display console.
#include using namespace std; int main() < int age ; cout > age; coutAll programming language have structure and syntax that we have to follow so that the program is legal, but that’s not important right now. So don’t worry about the details of the code, let’s focus on the big picture . The code on lines 7, 8, and 9 are what we are interested in. What’s important is that you can see the order or Sequence of the operations:
Run this program several times and enter different ages. Make sure you enter a whole number since that’s what the program expects.
Pretty boring right? Yes, but the computer is doing exactly what we are telling it to do.
That was pretty easy. But if we were only limited to Sequence our programs would be very limited indeed. We have to have a way to make decisions based on certain conditions.
Now let’s modify this program so that it can decide whether a person can vote! We’ll assume that a person must be 18 years or older to vote.
So, let’s see how Selection works.
We’ll add logic so that if the age entered is 18 or greater then the program will display, “ You can vote.” and if the age entered is less than 18 then the program will display, “ Sorry, you can’t vote.” .
See the selection, we are selecting which operations to execute depending on what the value of age is. Pretty simple and useful too!
#include using namespace std; int main() < int age ; cout > age; if (age >= 18) coutNotice that on line 10 we added an if statement. If the expression in the parentheses is true then we display, “ You can vote. “
But what if the person’s age is not greater than 18? That’s where the else on line 12 comes in. In this case we display, “ Sorry, you can’t vote yet. “ . We made a yes/no or true/false decision and we selected the operations to execute based on that decision.
That was pretty easy . Notice how we combined Sequence and Selection to make our program more useful.
But, suppose there are 3 voters and we would like to ask each of them what their age is. We could copy and paste the code 3 times, right? Sure, but if we had 1000 voters the program would grow very large and become very hard to follow and change. That’s where Iteration comes in. We can use a loop to iterate 3 times. Programming languages all allow Iteration and many provide multiple ways to iterate. Let’s do it using a very simple for loop in C++.
So let’s rewrite the code one final time.
#include using namespace std; int main() < int age ; for (int count = 1; count > age; if (age >= 18) cout coutNotice that our original code is still there, we haven’t changed it. But we now added a new operation on line 7 that tells the program to count from 1 to 3 and execute everything from lines 9-15 that many times.
So, now we will be asked to enter the ages for 3 voters and each time we’ll know whether a voter can vote or note. Pretty cool!
Now our program is using Sequence to provide the order in which we execute our instructions. Selection to allow decisions to be made and Iteration to loop or repeat our instructions as many times as we need.
Congratulations!
You have just learned the 3 elements that all programming languages must support and you wrote a simple program in one of the most complex programming languages used today, C++.
We can combine these 3 simple elements to implement any algorithm – now that’s power!
Of course, there is much more to programming. As our problems grow larger and more complex, we need other elements to help us deal with the complexity. Some of these elements are classes, methods, functions, threads, and many others.
But remember, the core elements of programming are the simple, Sequence, Selection, and Iteration elements that we learned about – that’s what it’s all about!
Ready to learn more? Take a look at my Beginning C++ Programming – From Beginner to Beyond course. It’s got close to 40 hours of video training and is aimed to make you a competent C++ programmer. It’s one of the most popular courses of it’s kind on Udemy!
Frank J. Mitropoulos, Ph.D. has over 30 years of experience in the computer science and information technology fields. Frank earned B.S., M.S., and Ph.D. degrees in Computer Science and has worked both in industry and academia. Frank has taught hundreds of courses at the university level to thousands of both undergraduate and graduate students in both face-to-face and online modes. Frank has also taught dozens of professional seminars for private corporations such as Motorola, IBM, GE, American Express, Logica, and many others. In addition to his teaching experience, Frank also worked for 12 years in industry doing both application, compiler, and operating systems development as well as project management. In 2014, Frank was one of 13 professors invited by Apple to Apple Headquarters to discuss teaching strategies using Apple development tools. In addition to being a full professor, trainer, and mentor. Frank is a consultant in the areas of Mobile Application Development, Game Design, and Machine Learning, and assists many technology companies as a technical interviewer for applicants seeking intermediate and senior level IT positions. Frank enjoys developing computer games and has published games using gaming frameworks such as LibGDX, Corona, Cocos2DX, SpriteKit, SceneKit, Unity and Unreal. Frank's academic specialty is Aspect-Oriented programming and is a recognized expert in the field with dozens of publications in that area of computer science. Frank brings a wealth of both real-world and academic experience to make your learning experience productive, relevant, and fun!
Recently a student in my The Complete JavaScript Course for Developers course asked about the capabilities and limitations of JavaScript. Specifically, can JavaScript collect and handle data from a user in a mobile environment. The answer is an unequivocal “yes” …