A micro-cultivation licence allows you to produce cannabis plants and seeds, fresh and dried cannabis. You can use a grow surface area (plant canopy) of up to 200 m 2 for growing cannabis plants. The grow surface areas include:
Your size limit only includes operations areas where you'll be:
There's no size limit for areas used for non-cultivation activities and storage.
You need Health Canada's approval to add outdoor grow areas after you've received your licence. You won't be able to use the area until Health Canada approves it. After the grow areas are approved, you don't need to notify Health Canada if you decide not to use them.
A nursery licence allows you to produce cannabis plants and seeds for starting material. You can have up to 5 kg of harvested flowering heads at any time (except seeds). You must destroy flowering heads (except seeds), leaves and branches of the plants within 30 days of harvesting them.
You can use a grow surface area (plant canopy) of up to 50 m 2 for growing flowering and budding cannabis plants. The grow surface areas include:
Your size limit only includes operations areas where you'll be growing flowering and budding cannabis plants.
There is no size limit for:
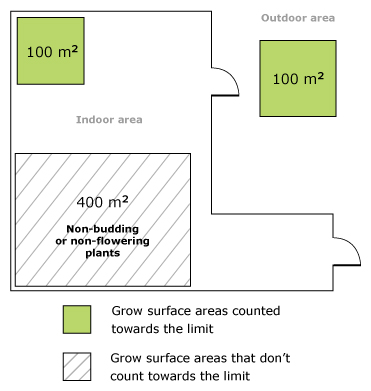
Figure 1 shows an example where the non-budding and non-flowering cannabis plants aren't included within the 50 m 2 size limit. The flowering and budding cannabis plants are only grown in the indoor area (20 m 2 ) and the outdoor area (25 m 2 ). The total grow surface area that counts towards the limit is 45 m 2 .

You need Health Canada's approval to add outdoor grow areas after you've received your licence. You won't be able to use the area until Health Canada approves it. After the grow areas are approved, you don't need to notify Health Canada if you decide not to use them.
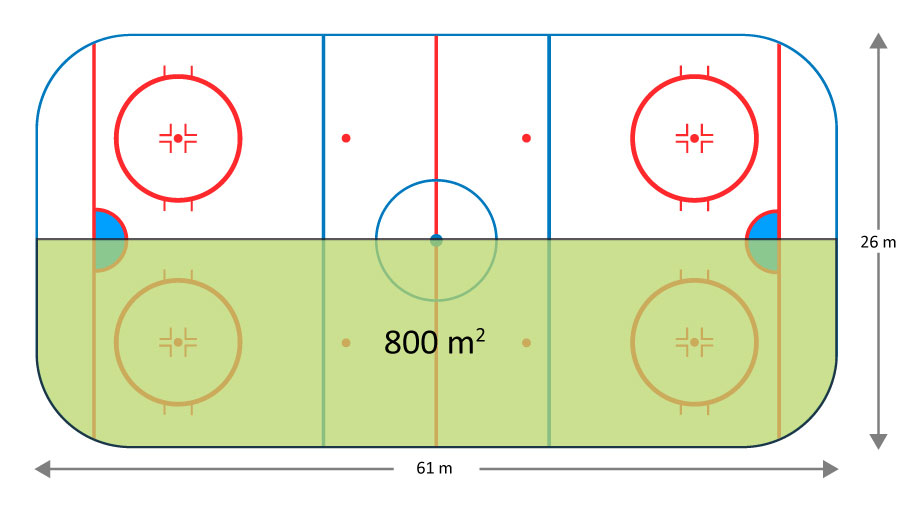
This section provides information on how you can calculate your total grow surface areas. Figure 2 represents what 200 m 2 looks like compared to a hockey rink.
You can calculate grow surface areas using different methods. You can combine these methods. Don't exclude areas or count them more than once. You'll need to provide your calculations in your site evidence package. For example, you can calculate:
Your total grow surface area can be made up of only indoor or outdoor grow areas, or both. The total grow surface areas in use can't exceed the size limit at any given time. If you use different areas according to the seasons, calculate your total grow surface area for those periods, such as during both the warmer and colder months.
The following operations areas and storage areas aren't included in the grow surface area calculations:
No matter how you decide to calculate your grow surface area, it needs to include all parts of the cannabis plant.
If you use the surface area of each cannabis plant to calculate your grow surface area, you need to include all parts of the plant. This includes all the leaves and branches, such as the canopy, the over-hanging leaves and branches. You will need to ensure that your grow surface area doesn't exceed the limit as your plants grow to their mature size. There's no limit on the height of the cannabis plants.
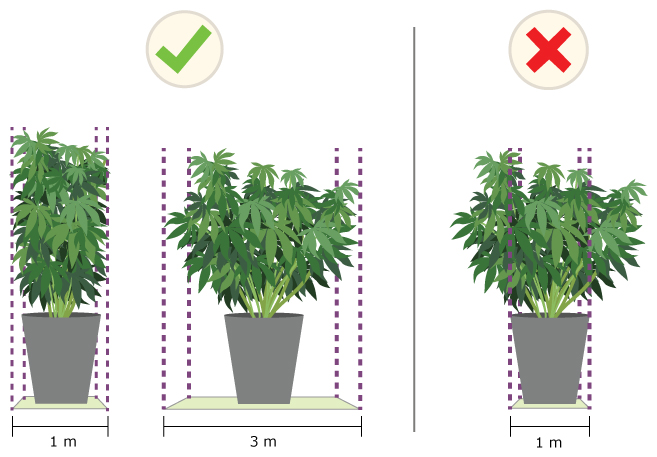
For example, Figure 3 shows 2 correct plant surface areas (left and centre) that include all the cannabis leaves and branches. The area on the right is wrong, as parts of the cannabis leaves and branches aren't included.
If you use the surface area of each piece of equipment, such as grow table or shelf to calculate your grow surface area, you need to include all parts of the plant. This includes all the leaves and branches, such as the canopy, the over-hanging leaves and branches. There's no limit on the height of the cannabis plants.
You also need to include all surfaces if the equipment unit has horizontal or vertical trays.
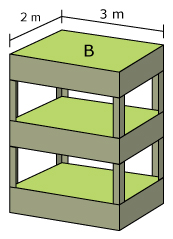
Figure 4 shows the total grow surface area of a shelf unit. This shelf unit has 3 trays, each is 6 m 2 (2 m by 3 m). This means that this shelf unit's grow area is 18 m 2 (numbers of trays multiplied by the surface area of 1 tray) if no part of the cannabis plant is over-hanging.
If you use the general grow area to calculate your grow surface area, you still need to include all parts of the plant. This includes all the leaves and branches, such as the canopy, the over-hanging leaves and branches.
You can calculate using the size of your indoor grow room or outdoor grow area. You can exclude non-grow areas such as the space between row crops.
Figure 5 shows a grow area where cannabis plants are grown in row crops. With 7 row crops of 10 metres by 2 metres, this grow surface area is 140 m 2 . You don't have to include the non-grow areas between the row crops in your surface area calculation.

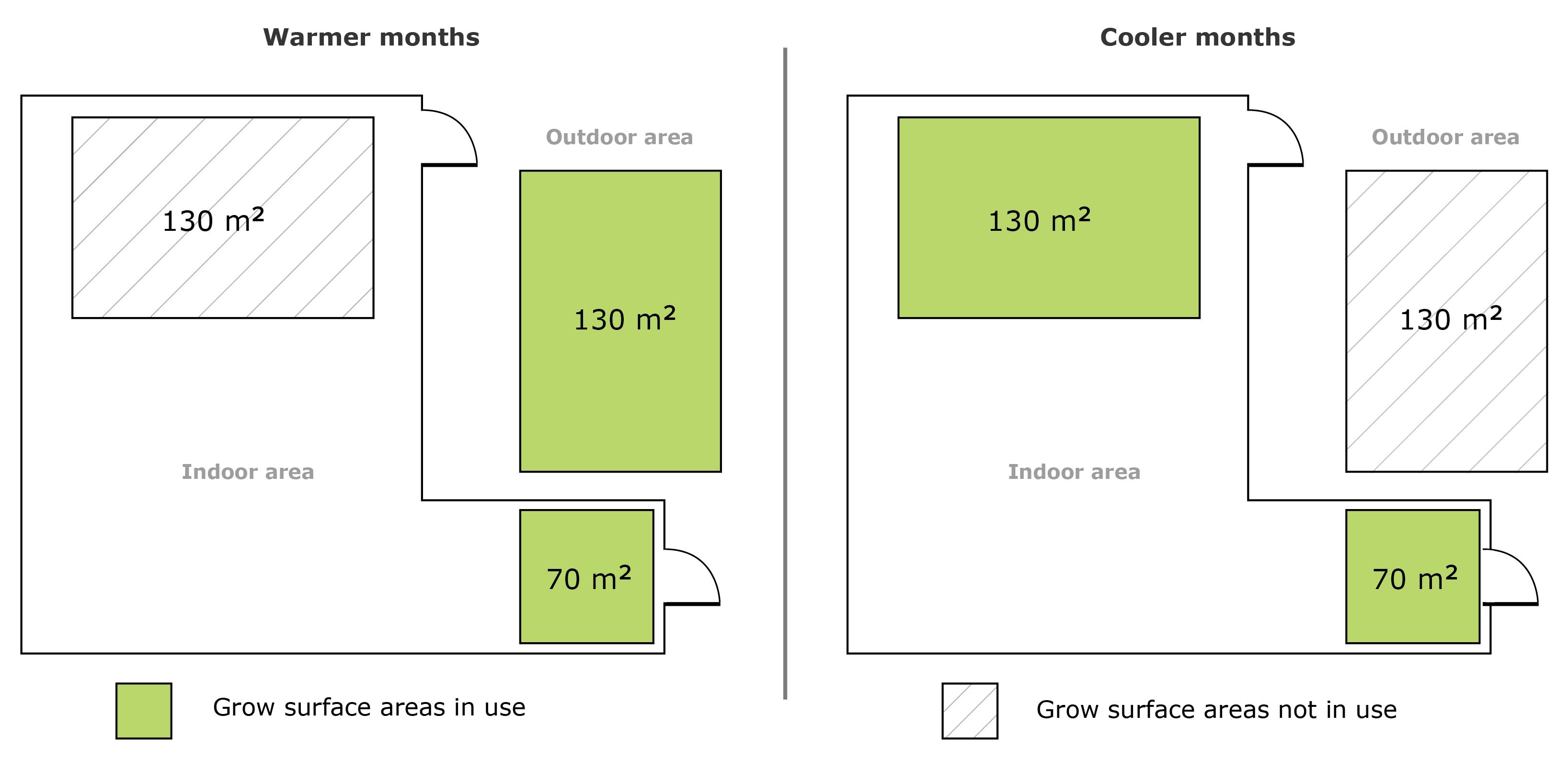
Figure 6 shows how a micro-cultivation licence can have a total of 330 m 2 of indoor (200 m 2 ) and outdoor (130 m 2 ) grow areas on their site. In the warmer months, they only use 70 m 2 of indoor grow areas and 130 m 2 of outdoor grow areas. During the cooler months, they only use 200 m 2 of indoor grow areas. Overall, they don't exceed the 200 m 2 size limit at any given time.
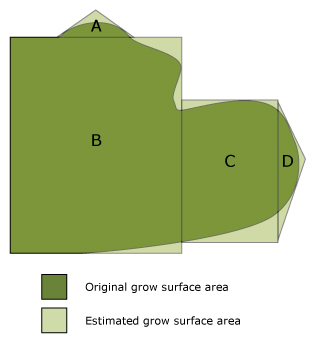
If it's hard to calculate the total surface of irregularly shaped grow areas, you can break it down into regular shapes (such as squares, rectangles and triangles). You can then calculate the surface area of each shape, and add the total surface areas to get an estimation. You'll need to show how your estimation is not an under-estimation.
Figure 7 shows an example of breaking up the total surface for an irregularly shaped grow area. The area is broken into regular shapes, 2 triangles and 2 rectangles. The smaller shapes cover more than the actual area.
Here's an example of how to calculate your grow surface area. A micro-cultivator has multiple types of grow areas, including:
Since the grow areas change in the warmer and colder months, the micro-cultivator will need to calculate the total grow surface area twice.
The micro-cultivator's total grow surface area during the warmer months is 192 m 2 . They're compliant with the 200 m 2 total surface grow area limit.
The micro-cultivator's total grow surface area during the colder months is 172 m 2 . They're compliant with the 200 m 2 total surface grow area limit.
Cannabis from the previous calendar year is included in the current year's possession limit. The licence holder can't be in possession of more than 600 kg of cannabis at any time.
A micro-processing licence allows you to produce all types of cannabis. You can possess up to 600 kg of dried cannabis (or its equivalent amount) in a calendar year.
The possession limit doesn't apply if the only cannabis you possess was grown from your own micro-cultivation licence at the same site. However, the limit will apply if you grow your own cannabis and get cannabis from other licence holders. This means that the total amount of cannabis you possess, including the cannabis grown on own site and from other licence holders, must not exceed the possession limit.
Cannabis plants and seeds don't count towards the possession limit.
If you receive other types of cannabis besides dried cannabis at your site, refer to the equivalency table to calculate your dried cannabis equivalency. The table lists the equivalent amount to 1 kg of dried cannabis for other types of cannabis. However, you may also need to refer to the definitions for the types of cannabis to help you determine which type it belongs to.
These general examples of types of cannabis are to help you determine the equivalency.
If you have both a micro-processing licence and a micro-cultivation licence at the same site, depending on whom you receive your cannabis from, the possession limit is calculated in 1 of 2 ways:
1. If you receive any cannabis (except plants and seeds) from other licence holders
The yearly possession limit of 600 kg of dried cannabis (or its equivalent amount) includes the total amount of the following:
This means you only possess cannabis harvested from your own micro-cultivation licence at the same site or receive only plants and seeds from other licence holders. In this case, the 600 kg possession limit does not apply. You can process all the fresh cannabis your micro-cultivation licence provides.
Calculating your possession limit can be divided into two steps.
Use the equivalency table and this formula to calculate your dried cannabis equivalent.
(Amount of one type of cannabis) divided by (Amount that is equivalent to 1 kg of dried cannabis)
Since this micro-processor has 120 kg of dried cannabis left over from the previous year, they can only possess 480 kg of dried cannabis this year (600 kg yearly possession limit minus 120 kg from previous year). In this example, since the micro-processor only possessed dried cannabis, there's no need to calculate the dried cannabis equivalency.
The formula to calculate the total dried cannabis possessed within 1 calendar year is:
Total amount of (cannabis from current calendar year) + (cannabis from the previous calendar year)
The micro-processor complied with the Cannabis Regulations because they didn't possess more than 600 kg of dried cannabis within 1 calendar year.
Example 2: A licence holder with a micro-processing licence and a micro-cultivation licence at the same site receives cannabis from other licence holders
A licence holder receives cannabis within a calendar year from their own micro-cultivation licence and from other licence holders. The breakdown is:
In this example, the steps to calculate the total dried cannabis possessed are:
The licence holder complied with the Cannabis Regulations because they didn't possess more than 600 kg of dried cannabis at any time in the calendar year.
Example 3: A licence holder with a micro-processing licence and a micro-cultivation licence at the same site that only receives cannabis plants and seeds from another licence holder
A licence holder with a micro-processing licence and a micro-cultivation licence at the same site receives the following cannabis in a calendar year:
In this example, the only cannabis the licence holder received from another licence holder were plants and seeds. The cannabis they possessed is from their own micro-cultivation licence at the same site, so the possession limit doesn't apply. As a result, the licence holder complied with the Cannabis Regulations even though they possessed more than 600 kg of dried cannabis within 1 calendar year.
Micro-cultivation, nursery and micro-processing licences can start with a modest-sized site and scale up later to a standard cultivation or standard processing licence. Scaling up to a standard licence will remove the grow area limit or possession limit, depending on your initial licence.
If your micro-cultivation, nursery and micro-processing licence application is being processed and you want to change to a standard licence application, there are 2 methods to do this.
Important: No matter which method you choose, you will have to pay another application-screening fee for the standard licence application.
To withdraw, click on the delete button on the Licence application page in the CTLS. If you withdraw your licence application before starting a new standard licence application: