
Get started for free
A project plan is a series of formal documents that define the execution and control stages of a project. The plan includes considerations for risk management, resource management and communications, while also addressing scope, cost and schedule baselines. Project planning software is used by project managers to ensure that their plans are thorough and robust.
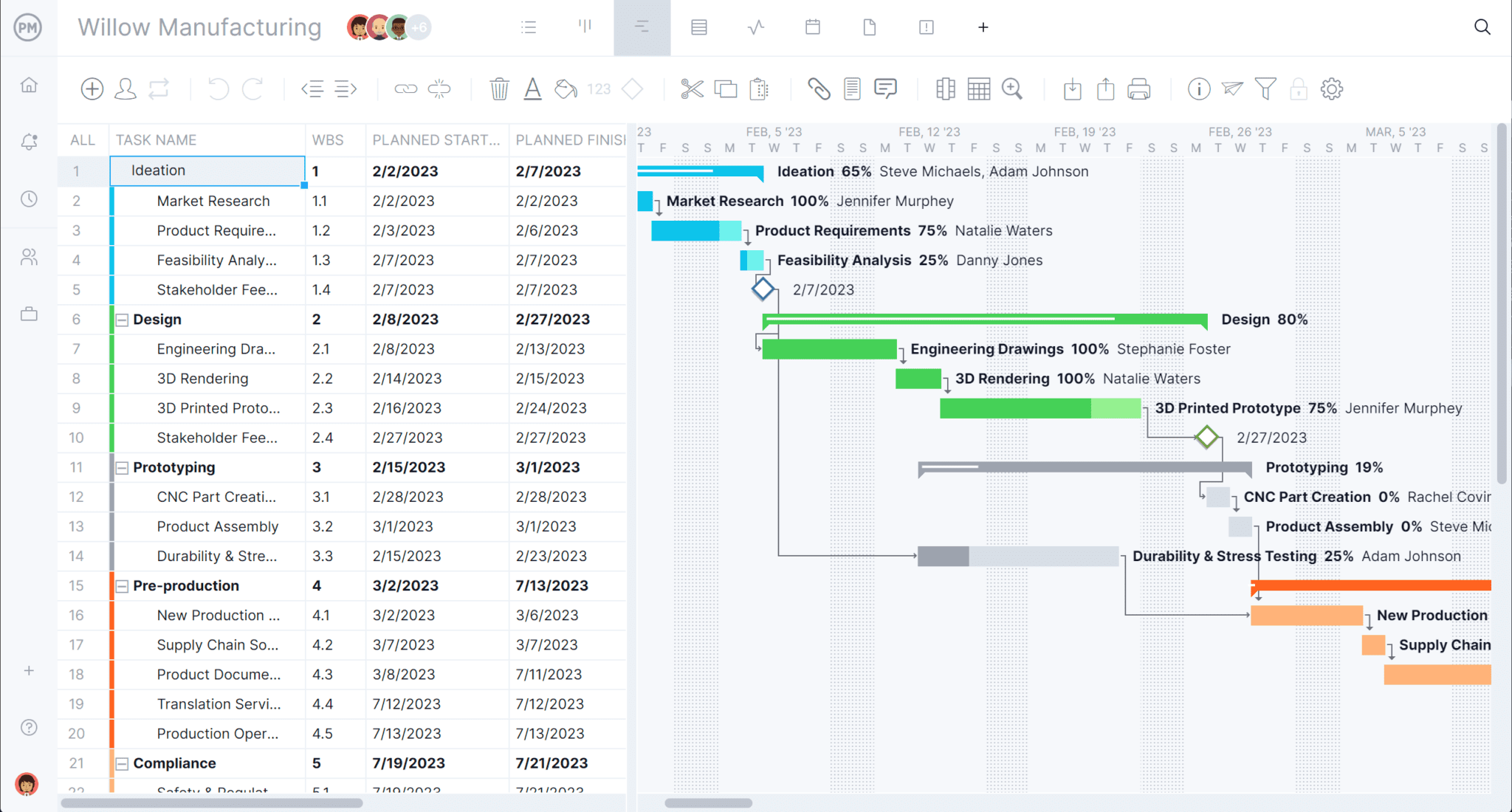
ProjectManager allows you to make detailed project plans with online Gantt charts that have task dependencies, resource hours, labor costs, milestones, the critical path and more. Plus, your team can execute the plan in any of our five project views, while you track progress along the way with dashboards. Start today for free.
The project plan, also called project management plan, answers the who, what, where, why, how and when of the project—it’s more than a Gantt chart with tasks and due dates. The purpose of a project plan is to guide the execution and control project phases.
As mentioned above, a project plan consists of the following documents:
This guide aims to give you all the information and resources you need to create a project plan and get it approved by your customers and stakeholders. Let’s start with the basics of writing a project plan.

Use this free Project Plan Template for Word to manage your projects better.
Download Word File
Your project plan is essential to the success of any project. Without one, your project may be susceptible to common project management issues such as missed deadlines, scope creep and cost overrun. While writing a project plan is somewhat labor intensive up front, the effort will pay dividends throughout the project life cycle.
The basic outline of any project plan can be summarized in these five steps:
Each of the steps to write a project plan explained above correspond to the 5 project phases, which we will outline in the next section.
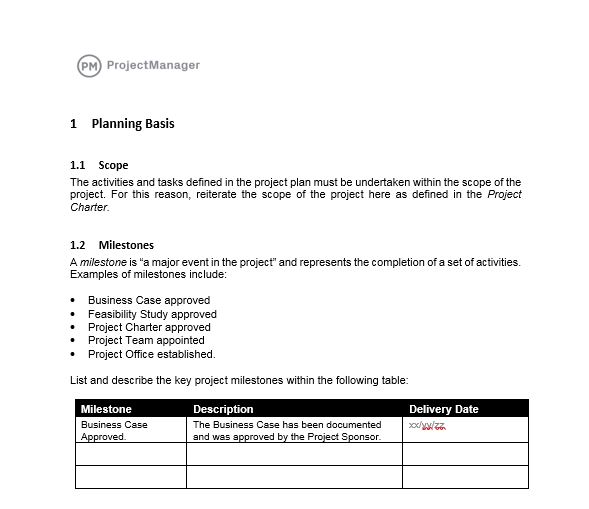
Any project, whether big or small, has the potential to be very complex. It’s much easier to break down all the necessary inclusions for a project plan by viewing your project in terms of phases. The Project Management Institute, within the Project Management Book of Knowledge (PMBOK), have identified the following 5 phases of a project:
Address all aspects of your project plan with this free project plan template for Word. This in-depth template will guide you through every phase of the project, as well as all the elements you need to outline for a proper document. Download your template today.
We’ve created also created other project planning templates to help you create all the different documents that make up a project plan, like the project schedule, project budget or resource plan.
Now that we’ve learned how to make a project plan, and identified the stages of the project management life cycle, we need to emphasize on the importance of the project planning phase.
The project planning process is critical for any kind of project because this is where you create all the documents that will guide how you’ll execute your project plan and how you’ll control risks and any issues that might occur. These documents, which are part of the project management plan, cover all the details of your project without exception.
There are project plan templates out there that can help you organize your tasks and begin the project planning process—but we here at ProjectManager recommend the use of project planning software. The feature set is far more robust and integrated with every project phase compared to an Excel project plan template, and is a great way to ensure your actual progress stays aligned with your planned progress.
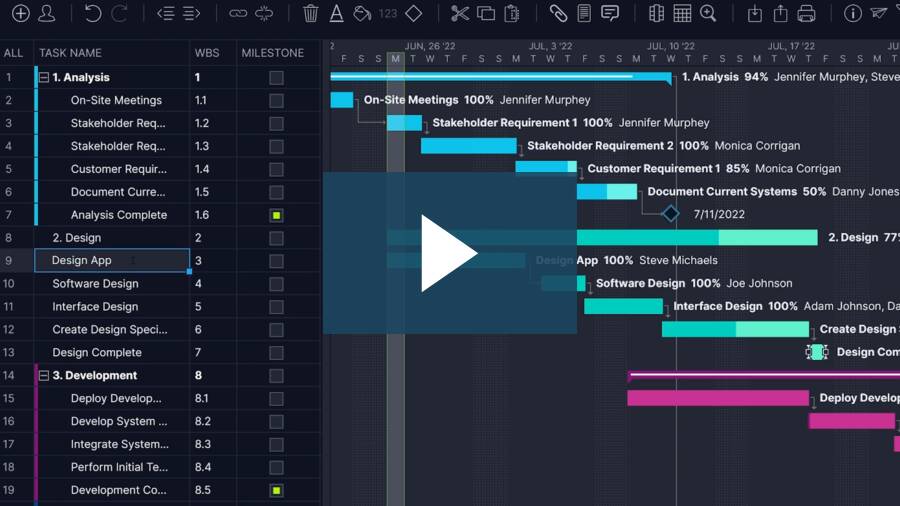
Once you write a project plan, it’s time for implementation. Watch the video below to see how project planning software helps organize a project’s tasks, resources and costs.
Project planning tools has become an invaluable tool for project managers in recent years, as it provides them the ability to maintain and automate the components we outlined above. Project planning software is a great tool to facilitate project management processes such as schedule development, team management, cost estimation, resource allocation and risk monitoring. Beyond that, planning software also allows managers to monitor and track their plan as it moves through the execution phase of the project. These features include dashboards, for a high-level view of the project’s progress and performance, and in-depth reports that can be used to communicate with stakeholders. Project planning software comes in all different sizes and shapes. There are some that focus on a single aspect, and others that offer a suite of planning features that can be used in each one of the project planning steps. What’s right for your project depends on your specific needs, but in general terms, project planning software is a much more powerful tool than project planning templates. Related: 20 Must-Have Project Management Excel Templates
A Gantt chart is the most essential tool for the project planning process. Organize tasks, add their duration and they automatically populate a project timeline. Set milestones to break the larger project into manageable phases, and link task dependencies to avoid bottlenecks later in the project.
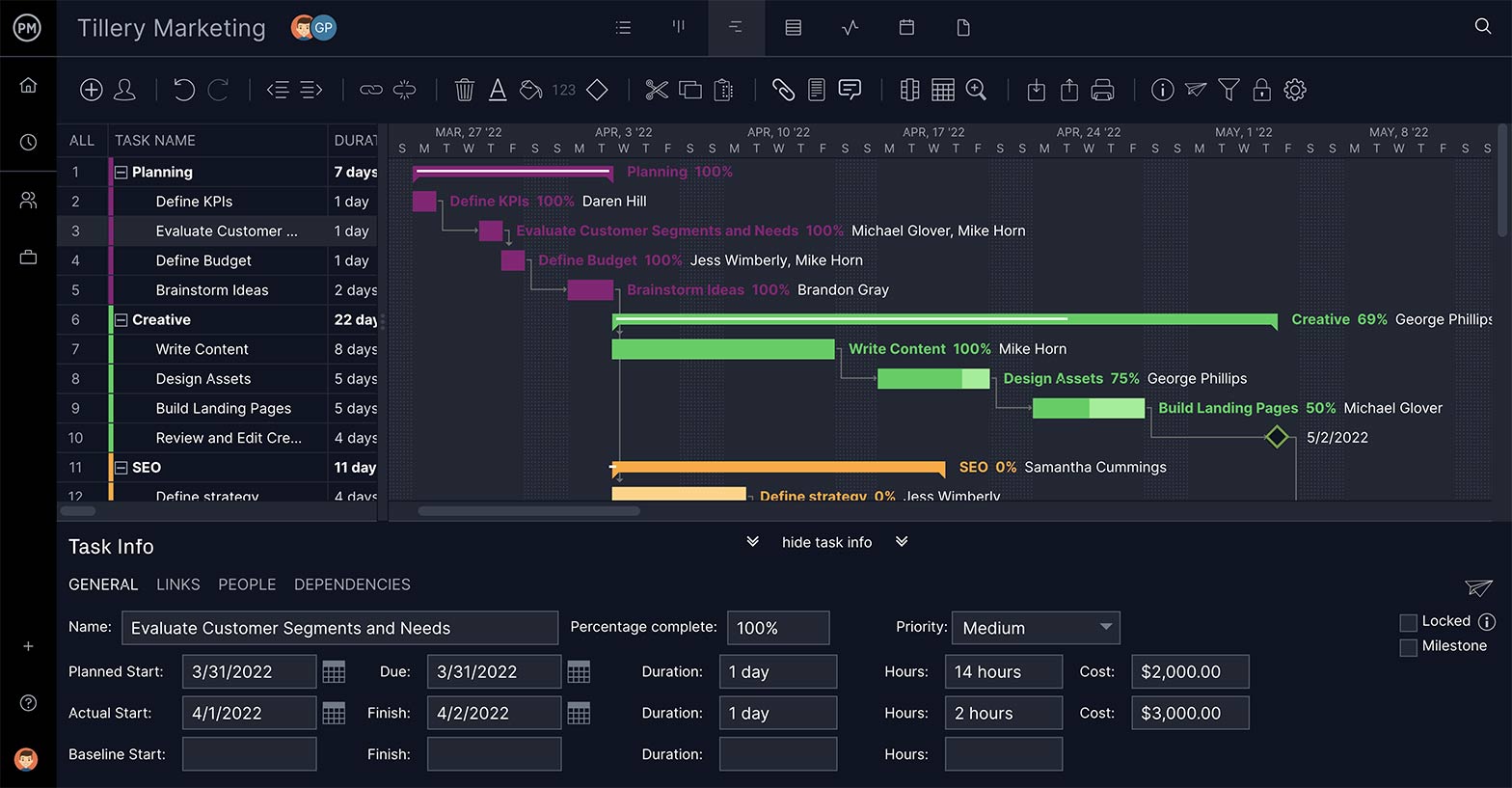
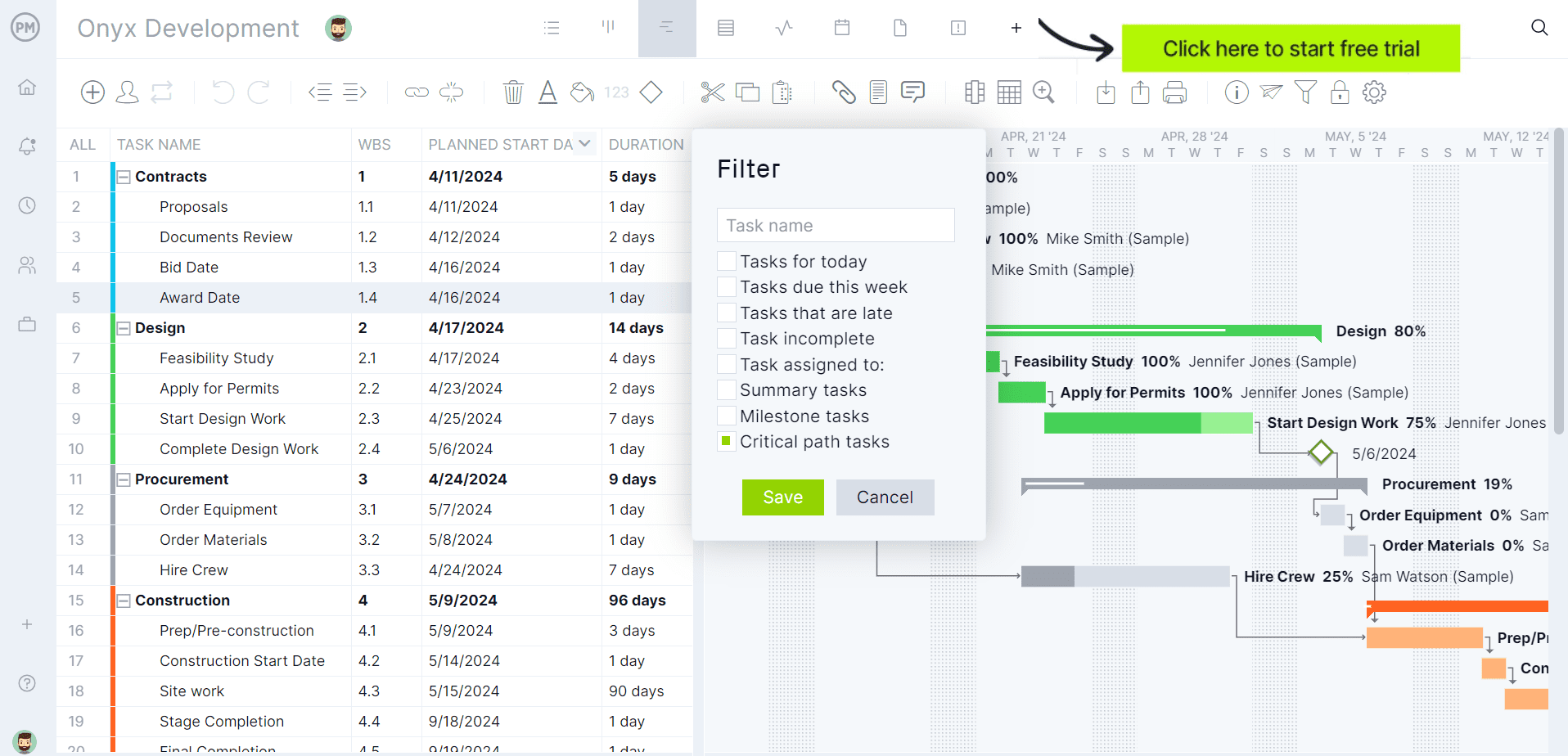
When planning a project, you need more than a to-do list. Seek out a planning software with a task list feature that lets you set priority levels, filters and collaborate. It’s a big plus if you can also make personal task lists that are private to manage your own work.
 s task list view" width="1554" height="874" />
s task list view" width="1554" height="874" />
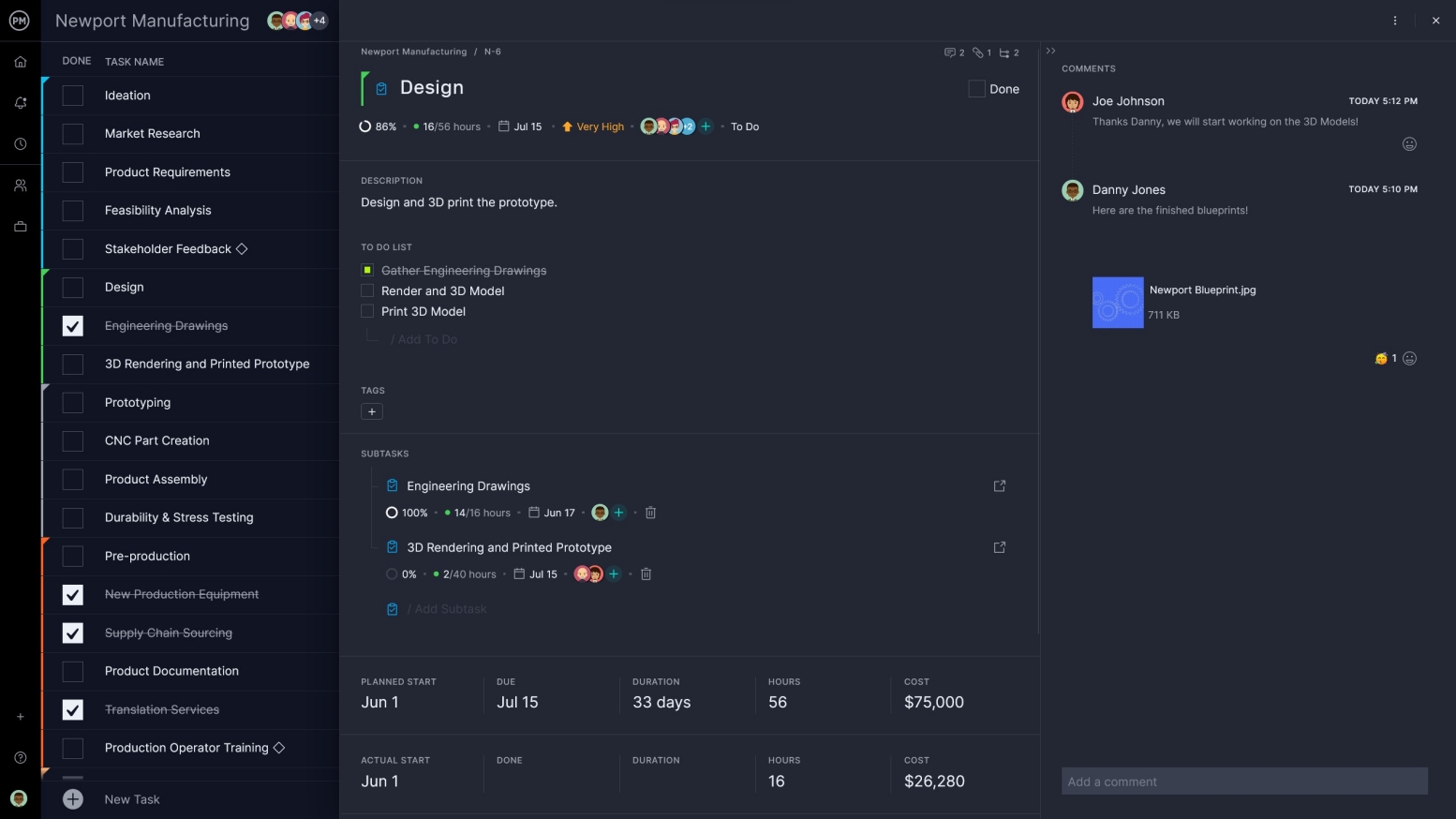
Workflows ensure proper execution of your plan, and no feature does this better than kanban boards. Customize boards to match your workflow and drag and drop cards as teams get their work done. See what work needs to be done and keep the focus on productivity with this feature.
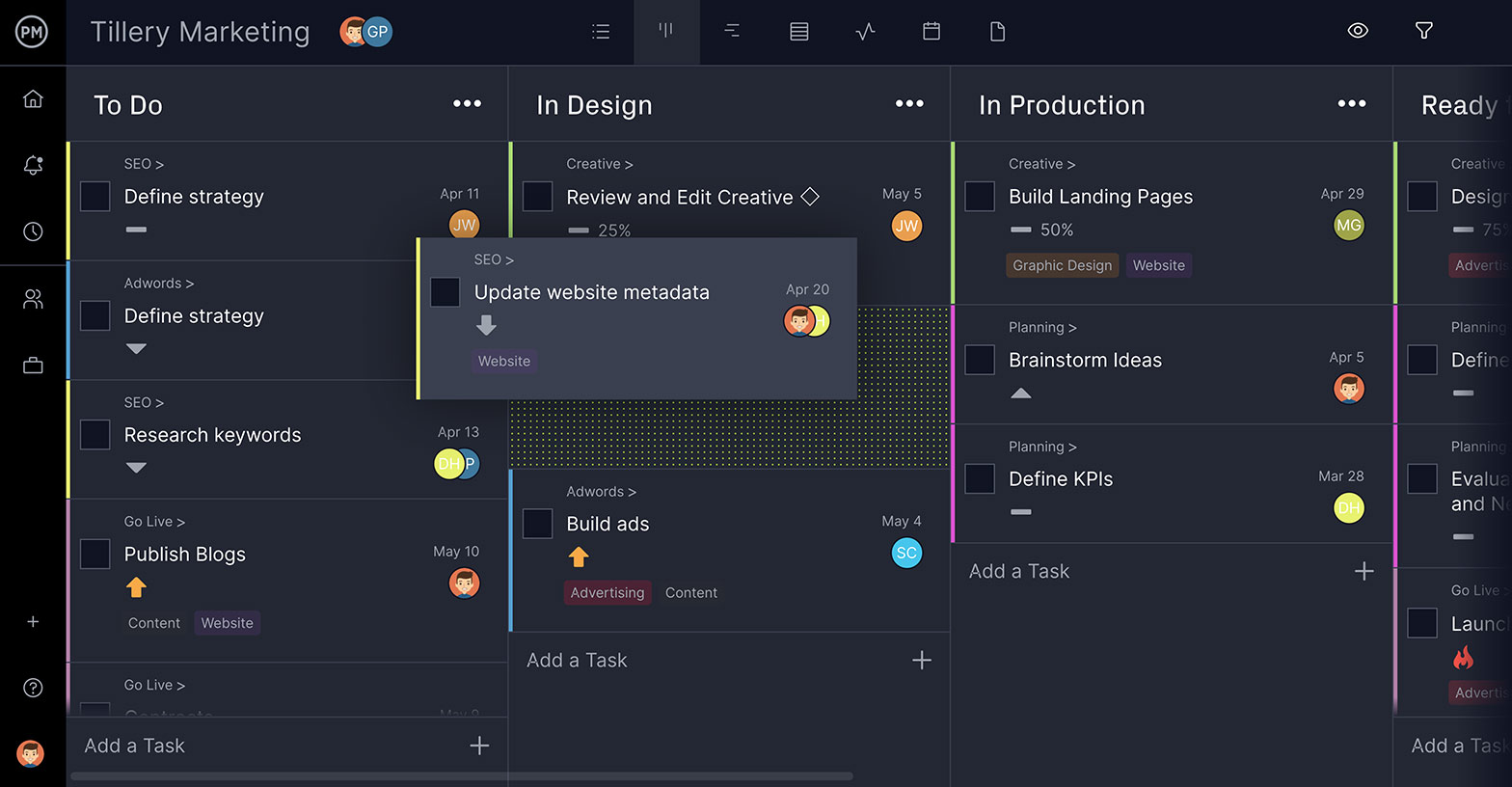
A dashboard can keep your project plan on track. Try and find a dashboard that’s synced with your planning tools, so everything updates automatically. It will make reporting easier too.

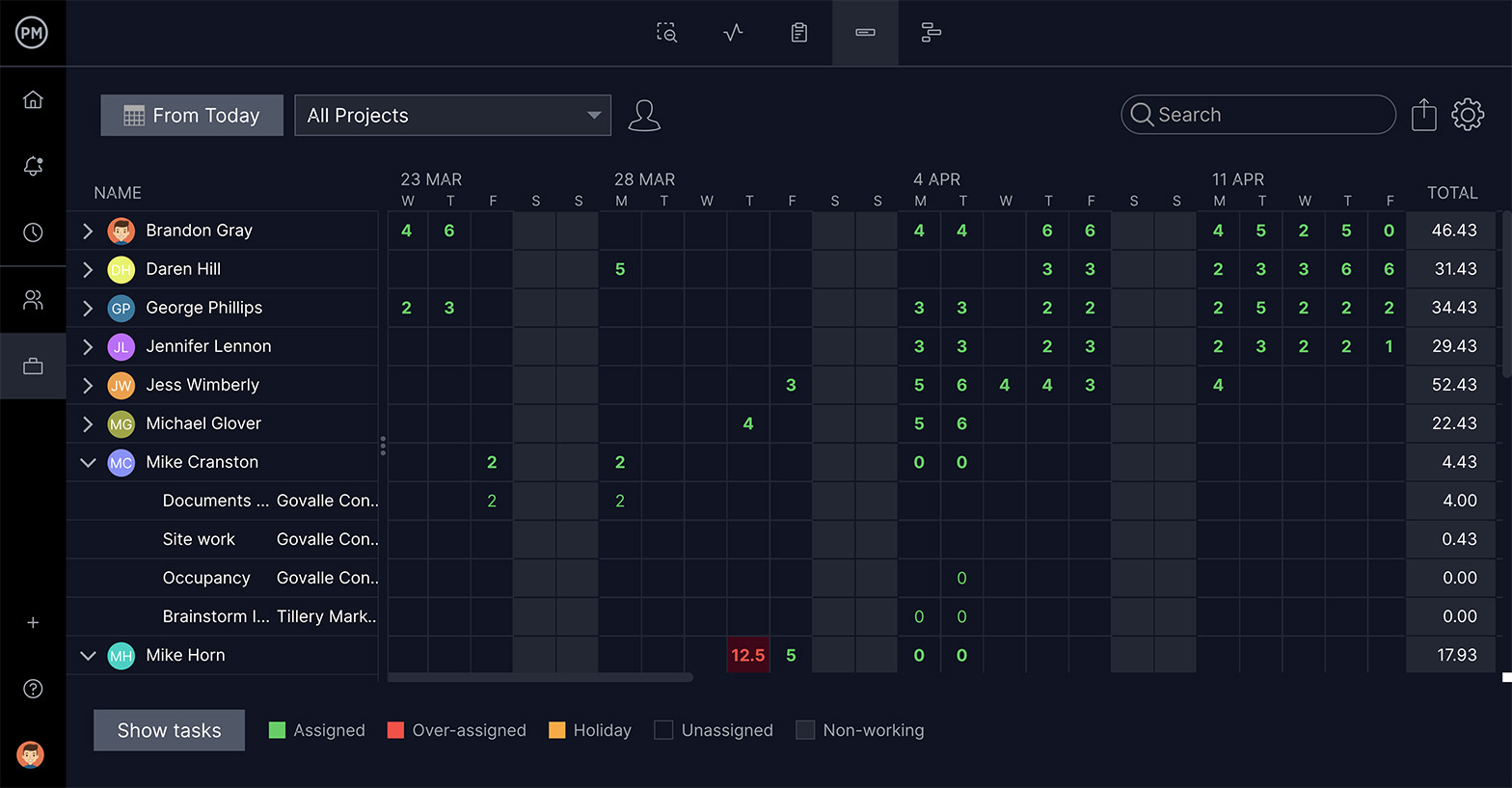
For a plan to go smoothly, you have to know what your team is working on. Find a way to balance your team’s availability with the project schedule. Workload features that map out resource allocation and holidays can be a big help here.
Rarely do you need to only focus on one project at a time. Give yourself the flexibility to manage multiple projects at once in the same tool. A roadmap feature that maps all of your projects on one timeline can be a lifesaver.
Before we dive into how to create a project plan, it helps to be familiar with some of the terms that you’ll run across. Here is a list of general terms you’ll encounter in this guide.
The project planning process is critical for the success of your project, and as a project manager, you have to think about all the elements that make up your project management plan such as work, time, resources and risks.
Now, we’re going to take you through the main project planning steps:
By following these project planning steps, you’ll clarify what you need to achieve, work out the processes you need to get there and develop an action plan for how you are going to take this project plan outline forward.
If you have a project, there’s a reason for it—that’s your business case. The business case outlines reasons why the project is being initiated, its benefits and the return on investment. If there’s a problem that is being solved, then that problem is outlined here. The business case will be presented to those who make decisions at your organization, explaining what has to be done, and how, along with a feasibility study to assess the practicality of the project. If approved, you have a project.
Every project has stakeholders, those who have a vested interest in the project. From the ones who profit from it, to the project team members who are responsible for its success. Therefore, any project manager must identify who these key stakeholders are during the project planning process, from customers to regulators. Meeting with them is crucial to get a better picture of what the project management plan should include and what is expected from the final deliverable.
It refers to the work required to accomplish the project objectives and generate the required deliverables. The project scope should be defined and organized by a work breakdown structure (WBS). Therefore, the project scope includes what you must do in the project (deliverables, sub deliverables, work packages, action items), but also what is nonessential. The latter is important for the project plan, because knowing what isn’t high priority helps to avoid scope creep; that is, using valuable resources for something that isn’t key to your project’s success.
You’ll need a capable project team to help you create your project plan and execute it successfully. It’s advisable to gather a diverse group of experienced professionals to build a multi-disciplinary team that sees your project management plan from different perspectives.
Once you define your project scope, you’ll have a task list that must be completed to deliver your project successfully. To do so, you’ll need resources such as equipment, materials, human capital, and of course, money. Your project budget will pay for all this. The first step to create a project budget is to estimate the costs associated with each task. Once you have those estimated costs, you can establish a cost baseline, which is the base for your project budget.
Goals and objectives are different things when it comes to planning a project. Goals are the results you want to achieve, and are usually broad. Objectives, on the other hand, are more specific; measurable actions that must be taken to reach your goal. When creating a project plan, the goals and objectives naturally spring from the business case, but in this stage, you go into further detail. In a sense, you’re fine-tuning the goals set forth in the business case and creating tasks that are clearly defined. These goals and objectives are collected in a project charter, which you’ll use throughout the project life cycle.
A project can have numerous deliverables. A deliverable can be a good, service or result that is needed to complete a task, process, phase, subproject or project. For example, the final deliverable is the reason for the project, and once this deliverable is produced, the project is completed. As defined in the project scope, a project consists of subprojects, phases, work packages, activities and tasks, and each of these components can have a deliverable. The first thing to do is determine what the final deliverable is, and how you will know that the quality meets your stakeholder’s expectations. As for the other deliverables in the project, they must also be identified and someone on the team must be accountable for their successful completion.
The project schedule is what everything hangs on. From your tasks to your budget, it’s all defined by time. Schedules are made up by collecting all the tasks needed to reach your final deliverable, and setting them on a project timeline that ends at your deadline. This can make for an unruly job ahead, which is why schedules are broken into phases, indicated by milestones, which mark the end of one project phase and the beginning of the next.
The plan is set, but it still exists in the abstract until you take the tasks on your schedule and begin assigning them out to your team members. Their roles and responsibilities must be clearly defined, so they know what to do. Then, when you assign them tasks from your plan, they should be clear, with directions and any related documentation they will need to execute the tasks.
Every project has some level of risk. There are several types of risk such as scope risk, technical risks and schedule risk, among others. Even if your project plan is thorough, internal and external factors can impact your project’s time, cost and scope (triple constraint). Therefore, you need to regard your planning as flexible. There are many ways to prepare for risk, such as developing a change management plan, but for now, the most important thing to do is to track your progress throughout the execution phase by using project status reports and/or project planning software to monitor risk.
As discussed above, a project management plan is a document that’s made of several elements. Before we get into a detailed explanation of each of them, it’s important to understand that you should include them all to have a solid project plan. The components that you’ll need might vary depending on your project, but in general terms, you’ll need these main documents to create your project management plan:
Your ultimate goal is to ensure a successful project for your stakeholders. They’re invested, and will not be satisfied twiddling their thumbs without looking at project status reports to track progress. By constructing a work breakdown structure (WBS) during the project planning phase you can break down the project for them so that they understand how your project plan will be executed. Keeping stakeholders informed is important to manage their expectations and ensure that they’re satisfied. Having regular planning meetings where you present progress reports are a great way to show them that everything is moving forward as planned and to field any questions or concerns they might have. Your stakeholder management plan will specify how you’ll engage stakeholders in the project.
Project planning software is a tool that helps to plan, organize and manage the schedule and resources needed to complete a project. ProjectManager is an award-winning project management software that organizes projects from planning to completion. Sign up for a free 30-day trial and follow along to build a thorough project plan that covers every detail.
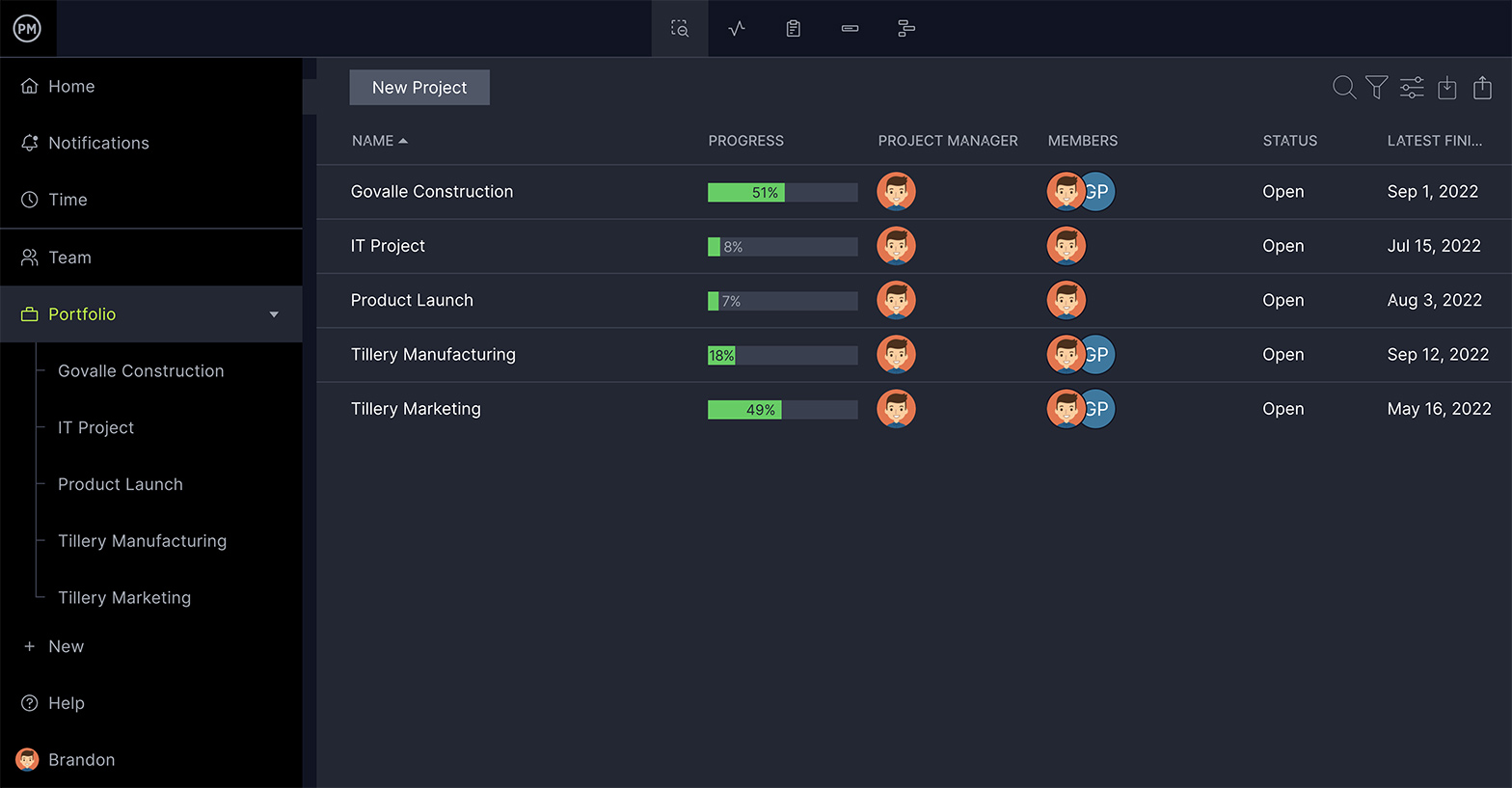
Tasks are the building blocks of any project and the start of any plan is identifying all the tasks that lead to your final deliverable.
Open the tool to add your tasks on the Gantt chart or one of the other multiple project views. You can import a task list from any spreadsheet or use one of our templates to get started.
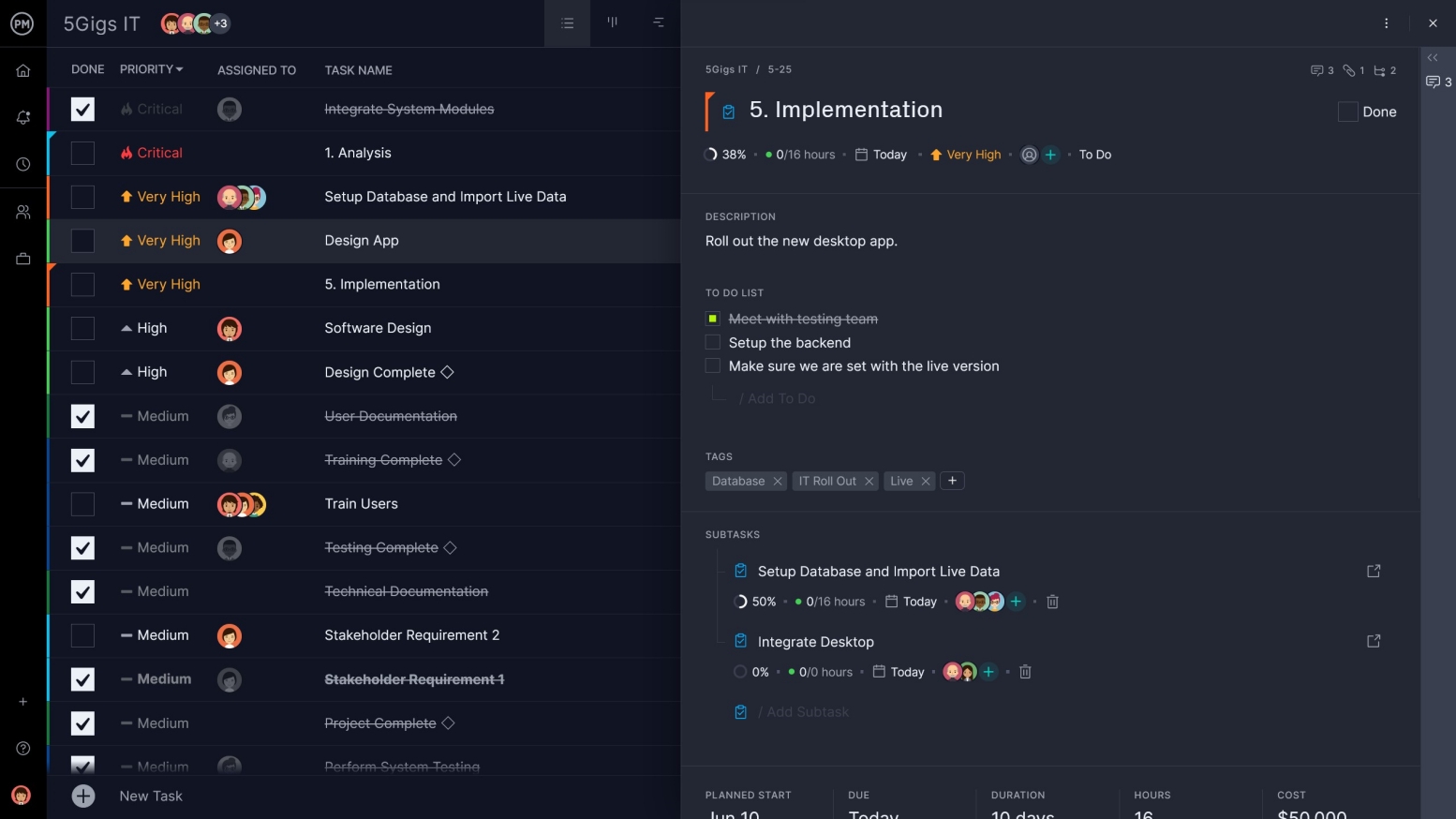
Every task has an estimated duration, which is the time it will take to complete it. They will also require a certain amount of funding, which needs to be collected to formulate your plan.
Add the start and end dates for each task in the Gantt and they populate a project timeline, so you can see the whole project laid out in one place. There’s also a column for task costs.
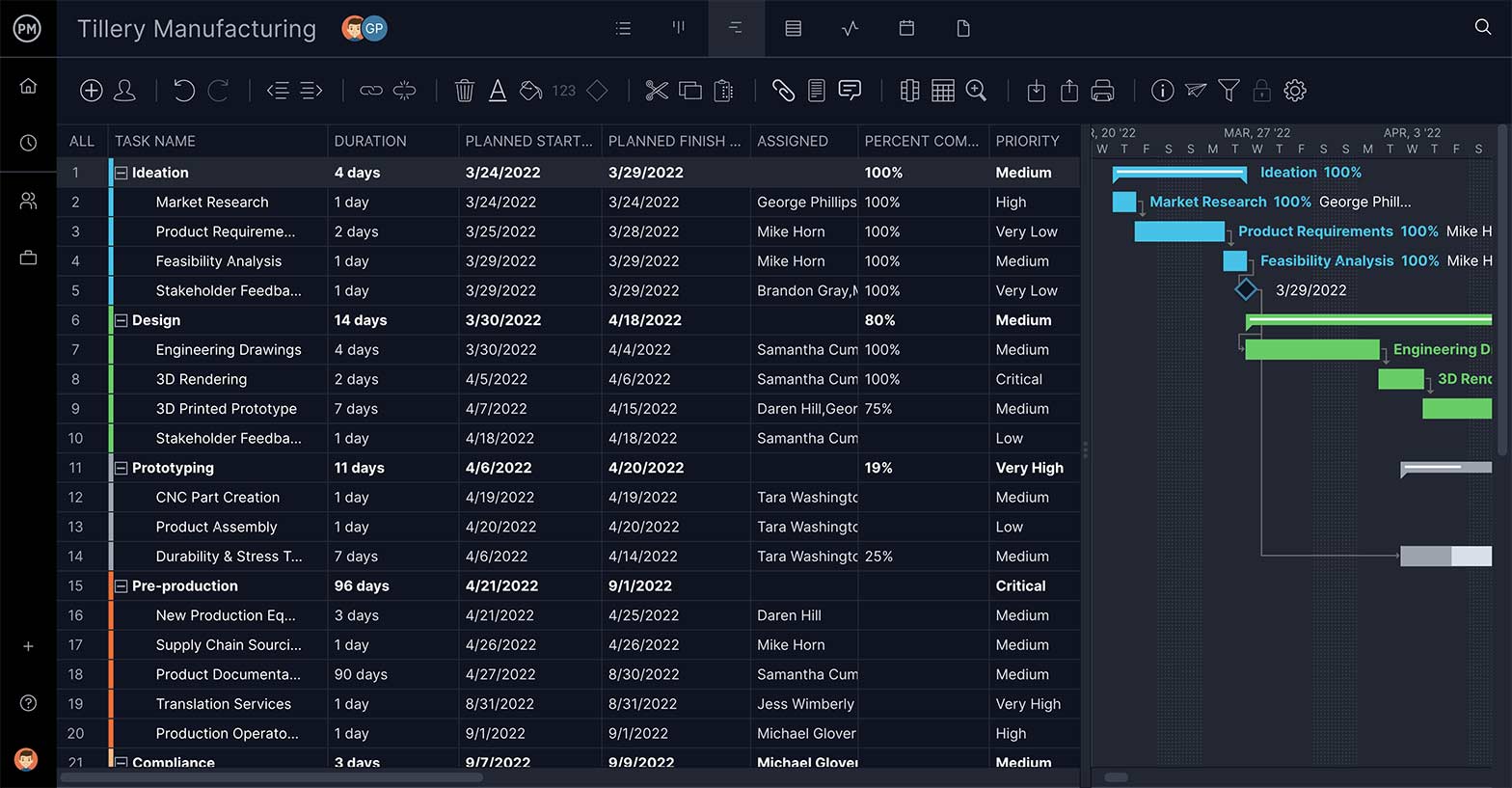
Tasks are not always separate from one another. Often one cannot start or stop until another has started or stopped. That’s called a task dependency and needs to be noted in your plan.
Link dependent tasks by dragging one to the other. A dotted line indicates that they’re linked, so you stay aware of the fact and can avoid bottlenecks later in the project.
A milestone indicates the end of one phase and the beginning of another, which helps with tracking and morale. The baseline sets your plan so you can compare it to actual progress.
There is a filter on the Gantt that automatically sets the baseline, so you can use it to track your actual progress against the plan. The baseline can also be locked with a click.
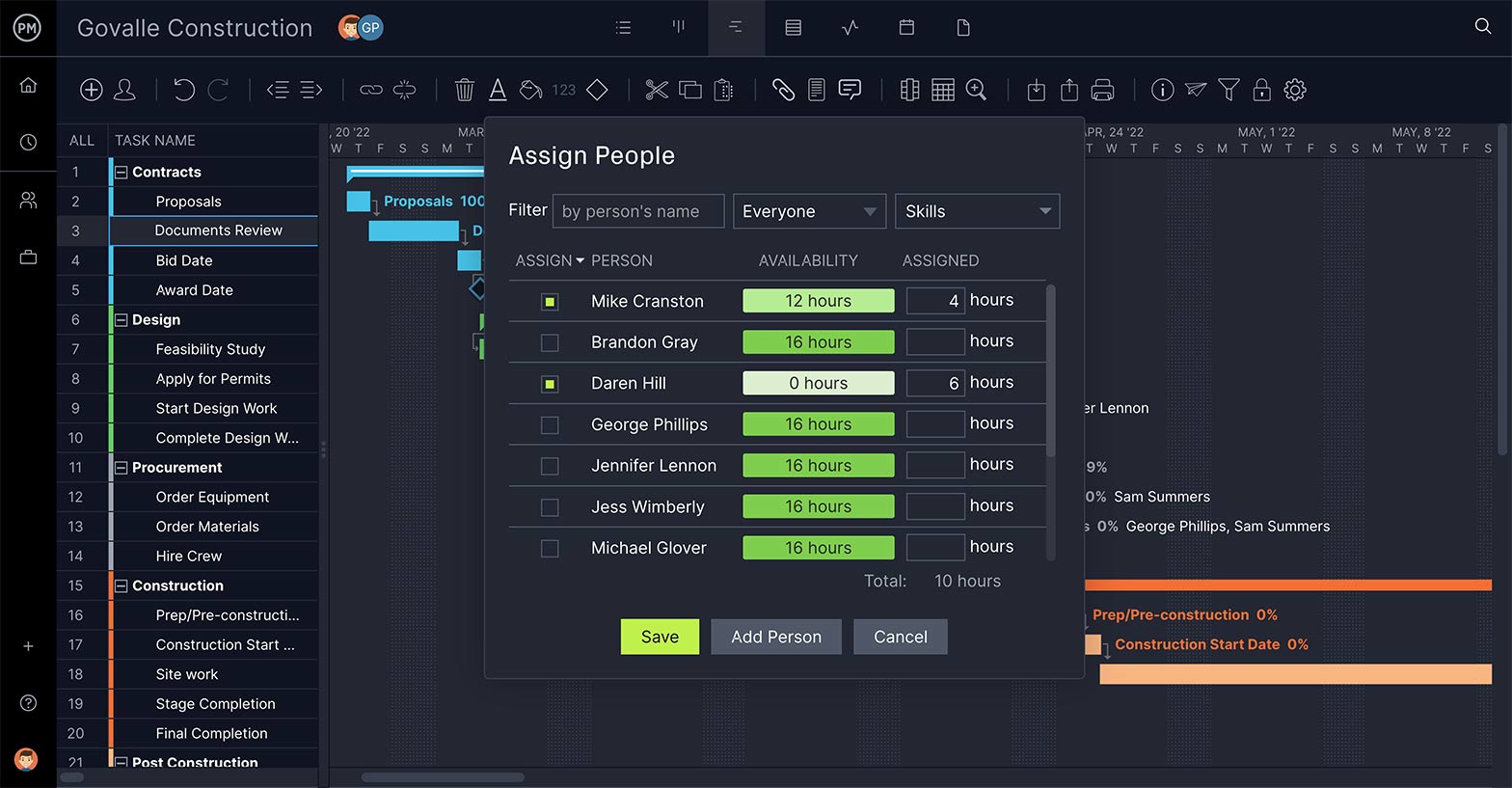
Getting the team and the tool together is how a project plan becomes actualized. The easier and seamless this transition, the faster you’ll get to work on the project.
Invite your team from the software and it generates an email with a link. Once they follow that link, they’re in and have access to the tools they need to manage their tasks.
Keeping track of your progress and then updating stakeholders is both how you stay on track and manage your stakeholders’ expectations.
See progress as it happens on our real-time dashboard, which calculates data and displays it over six project metrics. Reports can be filtered and shared for a deep dive into those numbers.

No plan remains the same throughout a project. Things happen and changes are demanded. Therefore, being able to edit your plan easily is key to the project planning process.
Edit your plan on the Gantt by a simple drag and drop. Move the old date to the new date and not only is that task fixed, but any impacted tasks are also updated automatically.
ProjectManager is an award-winning software that helps managers plan and helps teams get organized. Gantt charts control all aspects of your project plan from scheduling to assigning tasks and even monitoring progress. Multiple project views provide transparency into workflow and give everyone the tools they need to be at their best.
The project manager is responsible for producing the project plan, and while you can’t make up all the content yourself, you’ll be the one banging the keys to type it all out. Use templates where you can to save time. Download our free project plan template and write your plan in double-quick time!
The purpose of a project management plan is to serve as a guide for the execution and control phases. The project plan provides all the information necessary for the execution phase such as the project’s goals, objectives, scope of work, milestones, risks and resources. Then, this information helps project managers monitor and control the progress of the project.
We plan at the beginning to save time later. A good project plan means that you don’t have to worry about whether the project participants are going to be available on the right dates—because you’ve planned for them to be. You don’t have to worry about how to pay those invoices—you’ve planned your financial process. You don’t have to worry about whether everyone agrees on what a quality outcome looks like—you’ve already planned what quality measures you are going to use.
A good project plan sets out the processes that everyone is expected to follow, so it avoids a lot of headaches later. For example, if you specify that estimates are going to be worked out by subject matter experts based on their judgement, and that’s approved, later no one can complain that they wanted you to use a different estimating technique. They’ve known the deal since the start.
Project plans are also really helpful for monitoring progress. You can go back to them and check what you said you were going to do and how, comparing it to what you are actually doing. This gives you a good reality check and enables you to change course if you need to, bringing the project back on track.
Tools like dashboards can help you make sure that your project is proceeding according to plan. ProjectManager has a real-time dashboard that updates automatically whenever tasks are updated.
The project planning process already discussed only scratches the surface of what is a deep well of practices created to control your project. They start with dialogue — speaking to stakeholders, teams, et al.
The deliverable for your planning phase is a document called the project plan. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) – Fifth Edition says that the project plan is made up of lots of subsidiary plans. These include:
That’s a lot of documentation.
In reality, it’s rare that you’ll produce these as individual documents. What you need is a project plan that talks about the important elements of each of these. There’s no point creating a big document that sets out exactly how your business works anyway. If you already have a structured risk management process, then don’t waste time writing it all down again in your project plan.
Your project management plan needs to include enough information to make sure that you know exactly what processes and procedures need to be followed and who needs to be involved. Get your project plan approved by your stakeholders, your project sponsor and your team so there are no surprises later. As explained above, project planning charts and techniques such as Gantt charts, CPM, WBS or PERT can help you create your project plan.
This is hard to answer. It’s going to take longer to plan the moon landing than a new dating app.
The best way to estimate how long your project planning phase will take is to look at similar projects that have happened before, and see how long it took them to plan. Talk to the project manager as well, if you can, because they’ll have a view on whether that length of time was enough or not!
It’s easy to see how long other projects took if you have a project management tool that archives your old project schedules and makes the data available to everyone who needs it. You can then search for similar projects and study their schedules in detail.
A project plan is all about working out what to do and how to do it, so you need to get a lot of people involved. There are several good tools and project planning techniques for getting information from other people including:
You should also arm yourself with a task management tool, like a list or a kanban board. They are incredibly useful for noting down important things that should be in your project plan. Kanban board software can help structure your plan by writing down the key headings and then moving them around as required until you have a flow that looks right.

Finally, you’ll need an online project management system to store your project management plan in. Make sure that everyone in the team can access the latest version of the project plan.
Your project plan is not a document written in stone. You should be referring back to it and making changes to it as often as you need to. Parts of it, like your project schedule, will change almost daily. Other parts, like your procurement plans and cost management processes, won’t change at all during the life of your project.
The important thing to remember is that if your project management plan isn’t working for you, think about what you can do to change it. It’s there to guide your project management, not restrict you from doing the right thing. If you need to review how you manage work and project resources, then go back and review it. Make the changes you need, get the plan approved again and share it with the team.
Yes, this happens–most of the time! It’s rare to have all the information at the beginning of a project. Most managers want you to dive in and get started, but you might not have the luxury of knowing all the details.
That’s OK; we have techniques to help deal with uncertainty.
First is the project assumption. You use these to put caveats on your plan and to document the things that you assume to be true at this point in time. For example:
You get the picture. Then, if the design team comes back and says that they want the product to be a totally new palette of colors and that Marketing has to approve that, you are justified in saying that you’ll have to change the timescales on the schedule to make that possible.
You planned based on an assumption (that everyone agreed to, because you got the document approved) and that assumption turned out not to be true.
The most important thing to remember is that you shouldn’t rush the project planning process. Done properly, project planning takes time. And it’s worth doing it properly because if you don’t, we guarantee that you will hit problems later on as people won’t understand what they are supposed to do and why.
Great planning sets you up for success. It gives you the confidence of knowing that you’ve got all your processes, tools and systems in place to deliver the perfect result.
Now that you’ve learned all about project planning, it’s time to take action. Sign up for a free 30-day trial of ProjectManager and start planning your project today!